Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebihara, Kenichi; Sekine, Daiki*; Sakiyama, Yuji*; Takahashi, Jun*; Takai, Kenichi*; Omura, Tomohiko*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48(79), p.30949 - 30962, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)To understand hydrogen embrittlement (HE), which is one of the stress corrosion cracking of steel materials, it is necessary to know the H distribution in steel, which can be effectively interpreted by numerical simulation of thermal desorption spectra. In weld metals and TRIP steels, residual austenite significantly influences the spectra, but a clear H distribution is not well known. In this study, an originally coded two-dimensional model was used to numerically simulate the previously reported spectra of high-carbon ferritic-austenitic duplex stainless steels, and it was found that H is mainly trapped at the carbide surface when the amount of H in the steel is low and at the duplex interface when the amount of H is high. It was also found that the thickness dependence of the H desorption peak for the interface trap site is caused by a different reason than the conventional one.
Ebihara, Kenichi
Zairyo, 71(5), p.481 - 487, 2022/05
no abstracts in English
Ebihara, Kenichi; Sugiyama, Yuri*; Matsumoto, Ryosuke*; Takai, Kenichi*; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 52(1), p.257 - 269, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We simulated the thermal desorption spectra of a small-size iron specimen to which was applied during charging with hydrogen atoms using a model incorporating the behavior of vacancies and vacancy clusters. The model considered up to vacancy clusters 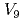 , which is composed of nine vacancies and employed the parameters based on atomistic calculations, including the H trapping energy of vacancies and vacancy clusters that we estimated using the molecular static calculation. As a result, we revealed that the model could, on the whole, reproduced the experimental spectra except two characteristic differences, and also the dependence of the spectra on the aging temperature. By examining the cause of the differences, the possibilities that the diffusion of clusters of
, which is composed of nine vacancies and employed the parameters based on atomistic calculations, including the H trapping energy of vacancies and vacancy clusters that we estimated using the molecular static calculation. As a result, we revealed that the model could, on the whole, reproduced the experimental spectra except two characteristic differences, and also the dependence of the spectra on the aging temperature. By examining the cause of the differences, the possibilities that the diffusion of clusters of 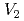 and
and 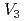 is slower than the model and that vacancy clusters are generated by applying strain and H charging concurrently were indicated.
is slower than the model and that vacancy clusters are generated by applying strain and H charging concurrently were indicated.
Saito, Kei*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Takai, Kenichi*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 50(11), p.5091 - 5102, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:84.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An attempt was made to separate and identify hydrogen peaks desorbed from lattice defects formed by plastic-strain in the presence of hydrogen in tempered martensitic steel showing quasi-cleavage fracture using thermal desorption spectroscopy from a low temperature (L-TDS) and positron annihilation spectroscopy (PAS). The L-TDS results made it possible to separate two peaks, namely, that of the original desorption and also that of new desorption. The PAS results revealed that the new desorption obtained by L-TDS corresponded to vacancy-type defects. Hydrogen enhanced vacancy-type defect concentration, approximately 10 order in terms of atomic ratio, formed within 1.5 mm from the fracture surface, These results indicate that the accumulation of excess vacancy-type defects enhanced by hydrogen in the local region can lead to nanovoid nucleation and coalescence in plastic deformation, resulting in quasi-cleavage fracture of tempered martensitic steel.
order in terms of atomic ratio, formed within 1.5 mm from the fracture surface, These results indicate that the accumulation of excess vacancy-type defects enhanced by hydrogen in the local region can lead to nanovoid nucleation and coalescence in plastic deformation, resulting in quasi-cleavage fracture of tempered martensitic steel.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Keikinzoku, 68(11), p.596 - 602, 2018/11
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) is considered as one cause of stress corrosion cracking. HE is a serious problem in the development of high strength aluminum alloy as with steels. For understanding HE, it is inevitable to know hydrogen trapping states in the alloys and it can be identified using thermal desorption spectrometry of H. In this study, we numerically simulated thermal desorption spectra of hydrogen in aluminum for a cylindrical and a plate specimens and interpreted the desorption peaks included in them on the basis of the trap site concentration and the trap energy. As a result, we found that the peak at the lowest-temperature side can result from grain boundaries and confirmed that the reported interpretation for other peaks is reasonable. We also obtained the result showing the possibility that the trap site concentration of defects changes during heating the specimens. This result may give a suggestion for the interpretation of temperature desorption spectra of steels.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
"Suiso Zeika No Kihon Yoin To Tokusei Hyoka" Kenkyukai Hokokusho, p.57 - 61, 2018/09
no abstracts in English
Ebihara, Kenichi
Materia, 57(7), p.338 - 344, 2018/07
no abstracts in English
Sakaguchi, Aya*; Chiga, Haruka*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tsuruta, Haruo*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Geochemical Journal, 52(2), p.187 - 199, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.55(Geochemistry & Geophysics)An aerosol sample collected on the 15th of March 2011 at Kawasaki City (Kanagawa) was sequentially leached with seawater for 30 days. As a result, about 60% of the total  Cs was extracted. In addition, a surface soil sample collected from Kawamata Town (Fukushima) two months after the Fukushima accident, was leached for 223 days with a natural seawater, a 1:1 mixture of ultrapure water and seawater, and ultrapure water. Eventually, more than 15% of the total
Cs was extracted. In addition, a surface soil sample collected from Kawamata Town (Fukushima) two months after the Fukushima accident, was leached for 223 days with a natural seawater, a 1:1 mixture of ultrapure water and seawater, and ultrapure water. Eventually, more than 15% of the total  Cs in the surface soil sample was efficiently desorbed by seawater leaching. In comparison, about 9% of the total
Cs in the surface soil sample was efficiently desorbed by seawater leaching. In comparison, about 9% of the total  Cs was leached with 1:1 diluted seawater and less than 1% of the total
Cs was leached with 1:1 diluted seawater and less than 1% of the total  Cs was leached with ultrapure water over the 223 days. Overall,
Cs was leached with ultrapure water over the 223 days. Overall,  Cs and
Cs and  Cs showed similar leaching behaviour.
Cs showed similar leaching behaviour.
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao
Photon Factory Activity Report 2017, 3 Pages, 2018/00
When a solid is heated in vacuum, a part of the surface layer desorbs as ions, which is known as "surface ionization". In this report, we present the results for surface ionization of bulk cesium chloride (CsCl). When the positive potential was applied to the sample, we found that the Cs ions were desorbed at around 410
ions were desorbed at around 410  C, which is lower than the melting point of CsCl (645
C, which is lower than the melting point of CsCl (645  C). The low desorption temperature was explained by the changes in the work function of the CsCl surface. As an application, we also investigated the desorption of Cs
C). The low desorption temperature was explained by the changes in the work function of the CsCl surface. As an application, we also investigated the desorption of Cs ions from Cs-adsorbed soil. When Cs-adsorbed soil was heated at 460
ions from Cs-adsorbed soil. When Cs-adsorbed soil was heated at 460  C for 2 hours, about 13% of Cs was desorbed as Cs
C for 2 hours, about 13% of Cs was desorbed as Cs ions. The results suggest that the surface ionization would possibly be applied to the desorption of Cs from contaminated soil.
ions. The results suggest that the surface ionization would possibly be applied to the desorption of Cs from contaminated soil.
Tsuchida, Yutaka*; Ebihara, Kenichi
Tetsu To Hagane, 103(11), p.653 - 659, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.38(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)A single peak in thermal desorption profiles of hydrogen, which are measured in low-temperature thermal desorption spectrometry (L-TDS) for a very thin plate specimen of tempered martensitic steel, was reproduced successfully by the superposition of two Gaussian distributions. Then, the parameters concerning the detrapping rate constants for both peaks, which are trap energy and pre-exponential factor, were calculated using the Choo-Lee plot. We confirmed that Kissinger model incorporating the obtained parameters could simulate the two peaks. In addition, we reproduced the single peak well using the reaction-diffusion equation incorporating the obtained parameters and the appropriate trap site concentration. From the results, we interpreted that the one peak corresponds to dislocation and the other to grain-boundary.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 2016 International Hydrogen Conference (IHC 2016); Materials Performance in Hydrogen Environments, p.470 - 477, 2017/00
For understanding hydrogen (H) embrittlement of steels, it is necessary to infer the state that defects trap H in the steels. Thermal desorption spectra of H obtained by the thermal desorption spectrometry (TDS) are used for inferring such a state. Because the thermal desorption spectra include the influence of experimental conditions and hydrogen diffusion as well as information of the defects trapping H, it is necessary to interpret the spectra using the numerical simulation. In the presentation, we determined the detrapping and the trapping rate constants which are necessary for the simulation from the experimental spectra obtained for plate specimens which is so small that H diffusion is ignorable. Then we confirmed that the model using the obtained rate constants can simulate the spectra of larger cylindrical specimens, so that it was found that the rate constant for small specimens can be used for the simulation of the spectra for specimens of different shape or size.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
"Suiso Zeika No Kihon Yoin To Tokusei Hyoka Kenkyukai Chukan Hokokukai" Shimposium Yokoshu (USB Flash Drive), p.30 - 35, 2016/09
no abstracts in English
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
"Suiso Zeika No Kihon Yoin, Kaiseki To Hyoka" Shimposium Yokoshu (USB Flash Drive), p.27 - 33, 2015/09
The thermal desorption spectra which reflect the H segregation state can be obtained by heating a specimen including H at a constant rate. However, the simulation of spectra needs to extract information of the H segregation state because spectra is affected by experimental conditions and H diffusion. The detrapping activation energy E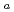 and the pre-exponential factor of detraping rate constant which are simulation parameters are fixed from the data previously reported or by fitting experimental spectra. Instead, we evaluated both of them from the experimental spectra of the specimen in which the H diffusion effect can be ignored, and simulated the spectra using them. As a result, in the case of iron, we could simulate spectra better than by the previous parameters. In the case of tempered martensitic steel, we could simulate spectra by the value obtained by adjusting the evaluated p
and the pre-exponential factor of detraping rate constant which are simulation parameters are fixed from the data previously reported or by fitting experimental spectra. Instead, we evaluated both of them from the experimental spectra of the specimen in which the H diffusion effect can be ignored, and simulated the spectra using them. As a result, in the case of iron, we could simulate spectra better than by the previous parameters. In the case of tempered martensitic steel, we could simulate spectra by the value obtained by adjusting the evaluated p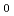 along with the evaluated E
along with the evaluated E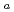 .
.
Doshida, Tomoki*; Suzuki, Hiroshi*; Takai, Kenichi*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Oshima, Nagayasu*
NanotechJapan Bulletin (Internet), 8(3), 5 Pages, 2015/07
Studying the creation and time evolution of defects is an important issue for interpreting the hydrogen embrittlement mechanism of steels. We have been studied the relationship between hydrogen embrittlement of high strength steel and lattice defects associated with hydrogen by thermal desorption analysis (TDA) and positron probe microanalyzer (PPMA).
Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Baba, Yuji; Izumi, Toshinori; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi
Clay Science, 18(3), p.71 - 77, 2014/09
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1379 - 1384, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)In facilities of ITER, various construction materials are possibly exposed by tritium during periodical maintenances and an accident. It is required to establish the effective surface decontamination methods for the above construction materials of ITER. In tritium decontaminating, so-called "soaking" effect is important. This effect is based on sorption of tritiated water on the materials and subsequent desorption from them. In order to obtain and summarize data on the amount of tritium adsorption on the various materials, a series of tritiated water vapor exposure experiments have been carried out as a function of time. The amounts of tritium adsorption on the materials saturated almost within the period from several weeks to 1 month. The adsorption rate of the epoxy was found to be the largest. In the exposure time less than 2 hrs, the adsorption coefficients for the examined materials were found to be in the same order as those reported by F.Ono. It will be also discussed from viewpoint of kinetics for adsorption and desorption.
Hirohata, Yuko*; Shibahara, Takahiro*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Arai, Takashi; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Masaki, Kei; Yagyu, Junichi; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Okuno, Kenji*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.557 - 560, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hirohata, Yuko*; Shibahara, Takahiro*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Arai, Takashi; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Yoshida, Hajime*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Yagyu, Junichi; Masaki, Kei; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.609 - 613, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Miya, Naoyuki; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Nishikawa, Masabumi*; Okuno, Kenji*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Oya, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.74 - 80, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Saeki, Masakatsu
JAERI-Review 2004-011, 54 Pages, 2004/03
In this review, experimental results on studies of radioactive iodine, tritium and neptunium are summarized. On studies of radioactive iodine, from various experimental results, the process establishing the formation mechanism of organic iodides was fully described. On the basis of formation mechanism, possibilities for the formation of organic iodides under nuclear reactor accidents and so on were also discussed. On studies of tritium, three topics were concisely described on the isotopic composition of tritium gases, the chemical forms and the diffusivity of tritium in various materials, and the sorption and desorption behaviors of tritium on surfaces of various materials. On the neptunium chemistry, the relationship between the structure of neptunium compound and the Moessbauer isomer shift and experimental results on neptunyl(VI) hydroxides were discussed.